 陶美凤
陶美凤
特别研究员
抗生素的生物合成及代谢调控
Email: tao_meifeng@sjtu.edu.cn
博士,研究员。本科毕业于武汉大学生物化学专业,博士毕业于华中农业大学生物化学与分子生物学专业。1999年始任教于华中农业大学,历任讲师、副教授、教授、博导。1999-2001年(每年6个月)到英国约翰.英纳斯中心(John Innes Centre)合作,从事链霉菌分化及其调控机理研究;2005-2007年在美国威斯康星大学(UW-Madison)药学院,从事微生物天然产物的化学生物学研究。2009年入选教育部新世纪优秀人才。2009年始任上海交通大学研究员/教授。主要从事微生物次级代谢调控机理、新药资源挖掘研究工作。
研究方向:
1 链霉菌分化和次级代谢调控机理的功能基因组研究:以模式菌天蓝色链霉菌和重要抗生素产生菌为研究对象,系统地揭示链霉菌形态分化和次级代谢的调控机理,新抗生素及其基因簇的高通量挖掘。
2 海洋微生物药物挖掘的新策略和新技术:瞄准海洋微生物新抗挖掘的关键瓶颈,全面优化现有宏基因组技术体系,突破传统大片段DNA克隆、穿梭和异源表达效率低的局限,发掘微生物—特别是海洋微生物的新药合成潜力。
3 微生物次级代谢途径解析及其途径工程:克隆新的抗生素生物合成途径,组合生物合成获得新抗生素衍生物以及天然产物合成。
4 抗生素高产育种的高新技术及其生产应用:以阿维菌素、多杀菌素、克拉维酸、雷帕霉素等重要抗生素高产育种为需求模式,拉网式筛选抗生素高产相关基因,将高产基因模块化,用于重排基因组,培育高产菌种,微生物新药高产的遗传机理与应用
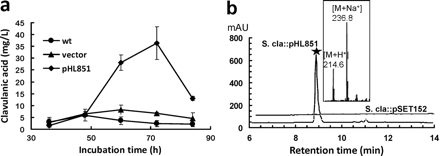
Fig 1 An additional copy of afsRScla increased clavulanic acid production and induced holomycin production in S. clavuligerus. (Chen, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012)
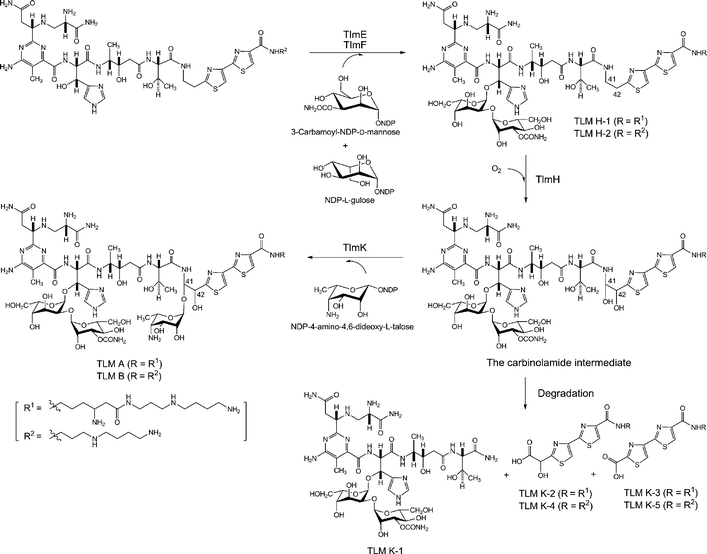
Fig 2 The revised pathway for TLM biosynthesis featuring TlmH-catalyzed hydroxylation of both C41 and C42 to afford labile carbinolamide intermediates and TlmK-catalyzed subsequent glycosylation of their hemiaminal hydroxyl groups as the final two steps. (Tao, et al. Mol Biosyst. 2010)
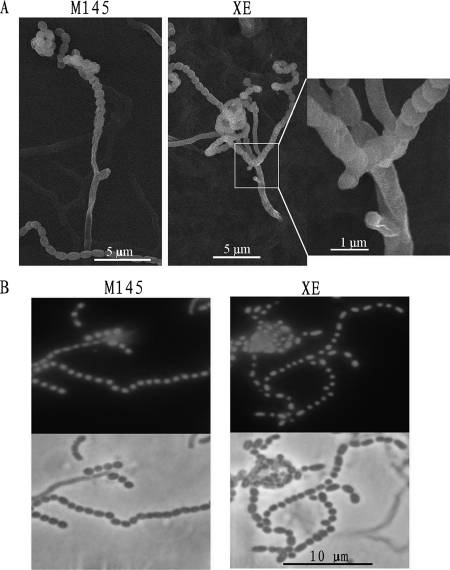
Fig 3 The cslASc gene affected aerial-hyphal development. (Xu, et al. J Bacteriol. 2008)
教育经历:
1994.09-1999.06 博士,华中农业大学生命科技学院/农业微生物学国家重点实验室
1988.09-1992.06 学士,武汉大学生物系生物化学专业
工作经历:
2009.01- 研究员,上海交通大学生命科学技术学院/微生物代谢国家重点实验室
1999.07-2008.12 讲师/副教授,华中农业大学生命科技学院/农业微生物学国家重点实验室
2005.03-2008.02 研究助理,美国威斯康星大学-麦迪逊分校药学院
1999.07-2002.03 (分段共18个月),访问学者,英国约翰英纳斯中心
1992.07-1994.08 技术员,广西桂林市第二制药厂
发表论文:
(1) Characterization of streptonigrin biosynthesis reveals a cryptic carboxyl methylation and an unusual oxidative cleavage of a N-C bond. Xu F, Kong D, He X, Zhang Z, Han M, Xie X, Wang P, Cheng H, Tao M, Zhang L, Deng Z, Lin S*, J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135(5):1739-48.
(2) A designer bleomycin with significantly improved DNA cleavage activity. Huang SX, Feng Z, Wang L, Galm U, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Yang D, Tao M, Coughlin JM, Duan Y, Shen B*, J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134(32):13501-9.
(3) High-throughput screening for Streptomyces antibiotic biosynthesis activators. Chen L, Wang Y, Guo H, Xu M, Deng Z, Tao M*. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2012, 78(12):4526-8.
(4) A non-restricting and non-methylating Escherichia coli strain for DNA cloning and high-throughput conjugation to Streptomyces coelicolor. Zhou H, Wang Y, Yu Y, Bai T, Chen L, Liu P, Guo H, Zhu C, Tao M*, Deng Z, Curr Microbiol, 2012, 64(2):185-90.
(5) Identification and characterization of the pyridomycin biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces pyridomyceticus NRRL B-2517. Huang T, Wang Y, Yin J, Du Y, Tao M, Xu J, Chen W, Lin S*, Deng Z, J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(23):20648-57.
(6) Comparative analysis of the biosynthetic gene clusters and pathways for three structurally related antitumor antibiotics: bleomycin, tallysomycin, and zorbamycin. Galm U, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Wang L, Huang SX, Unsin C, Tao M, Coughlin JM, Shen B*, .J Nat Prod, 2011, 74(3):526-36.
(7) Improved production of the tallysomycin H-1 in Streptoalloteichus hindustanus SB8005 strain by fermentation optimization. Zhang N, Zhu X, Yang D, Cai J, Tao M, Wang L, Duan Y, Shen B*, Xu Z*. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010, 86(5):1345-53.
(8) Functional characterization of tlmH in Streptoalloteichus hindustanus E465-94 ATCC 31158 unveiling new insight into tallysomycin biosynthesis and affording a novel bleomycin analog. Tao M†, Wang L†, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Zhang N, Yang D, Galm U, Coughlin JM, Xu Z, Shen B*, Mol Biosyst, 2010, 6(2):349-56.
(9) Characterization of the tunicamycin gene cluster unveiling unique steps involved in its biosynthesis. Chen W, Qu D, Zhai L, Tao M, Wang Y, Lin S, Price NP*, Deng Z*, Protein Cell. 2010, 1(12):1093-105.
(10) Functional characterization of tlmK unveiling unstable carbinolamide intermediates in the tallysomycin biosynthetic pathway. Wang L†, Tao M†, Wendt-Pienkoski E, Galm U, Coughlin JM, Shen B*, J Biol Chem, 2009, 284(13):8256-64.
(11) The biosynthetic gene cluster of zorbamycin, a member of the bleomycin family of antitumor antibiotics, from Streptomyces flavoviridis ATCC 21892. Galm U, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Wang L, George NP, Oh TJ, Yi F, Tao M, Coughlin JM, Shen B*, Mol Biosyst. 2009,5(1):77-90.
(12) In vivo manipulation of the bleomycin biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003 revealing new insights into its biosynthetic pathway. Galm U, Wang L, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Yang R, Liu W, Tao M, Coughlin JM, Shen B*, J Biol Chem, 2008, 283(42):28236-45.
(13) A cellulose synthase-like protein involved in hyphal tip growth and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces. Xu H, Chater KF, Deng Z, Tao M*, J Bacteriol, 2008, 190(14):4971-8.
(14) Sequences downstream of the start codon and their relations to G + C content and optimal growth temperature in prokaryotic genomes. Li W, Zou H, Tao M*, Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2007, 92(4):417-27.
(15) Glycopeptide antitumor antibiotic zorbamycin from Streptomyces flavoviridis ATCC 21892: strain improvement and structure elucidation. Wang L, Yun BS, George NP, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Galm U, Oh TJ, Coughlin JM, Zhang G, Tao M, Shen B*, J Nat Prod, 2007, 70(3):402-6.
(16) Role of an FtsK-like protein in genetic stability in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Wang L, Yu Y, He X, Zhou X, Deng Z, Chater KF, Tao M*, J Bacteriol, 2007, 189(6):2310-8.
(17) The tallysomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptoalloteichus hindustanus E465-94 ATCC 31158 unveiling new insights into the biosynthesis of the bleomycin family of antitumor antibiotics. Tao M, Wang L, Wendt-Pienkowski E, George NP, Galm U, Zhang G, Coughlin JM, Shen B*, Mol Biosyst, 2007, 3(1):60-74.
(18) A genetic and bioinformatic analysis of Streptomyces coelicolor genes containing TTA codons, possible targets for regulation by a developmentally significant tRNA. Li W, Wu J, Tao W, Zhao C, Wang Y, He X, Chandra G, Zhou X, Deng Z, Chater KF, Tao M*, FEMS Microbiol Lett, 2007, 266(1):20-8.
(19) Identification of a gene negatively affecting antibiotic production and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Li W, Ying X, Guo Y, Yu Z, Zhou X, Deng Z, Kieser H, Chater KF, Tao M*, J Bacteriol, 2006, 188(24):8368-75.
(20) A rare leucine codon in adpA is implicated in the morphological defect of bldA mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor. Takano E†, Tao M†, Long F, Bibb MJ, Wang L, Li W, Buttner MJ, Bibb MJ, Deng ZX, Chater KF*, Mol Microbiol, 2003, 50(2):475-86.
 陶美凤
陶美凤


