Metab Eng: halogenase for improved chlortetracycline biosynthesis
 Metab Eng. 2013 Jun 22. pii: S1096-7176(13)00063-3.
Metab Eng. 2013 Jun 22. pii: S1096-7176(13)00063-3.
Deciphering and engineering of the final step halogenase for improved chlortetracycline biosynthesis in industrial Streptomyces aureofaciens.
Zhu T, Cheng X, Liu Y, Deng Z, You D.
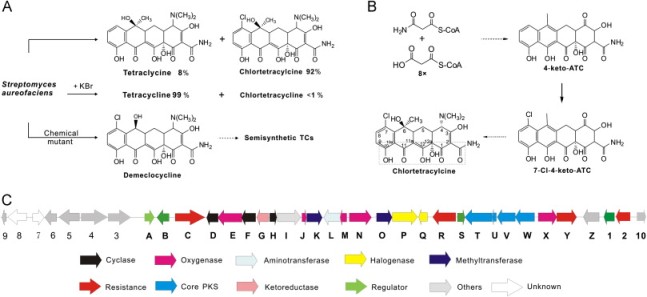
Chlortetracycline (CTC) is an important member from antibiotics tetracycline (TC) family, which inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria and is widely involved in clinical therapy, animal feeds and aquaculture. Previous works have reported intricately the biosynthesis of CTC from the intermediates in random mutants of Streptomyces aureofaciens and the crucial chlorination remained unclear. We have developed the genetic manipulation in an industrial producer, in which about 15.0g/l CTC predominated along with 1.2g/l TC, and discovered that chlorination by ctcP (an FADH2-dependent halogenase gene) is the last inefficient step during CTC biosynthesis. Firstly, the ΔctcP strain accumulated about 18.9g/l "clean" TC without KBr addition and abolished the production of CTC. Subsequently, CtcP was identified to exhibit a substrate stereo-specificity to absolute TC (4S) rather than TC (4R), with low kcat of 0.51±0.01min-1, while it could halogenate several TC analogs. Accordingly, we devised a strategy for overexpression of ctcP in S. aureofaciens and improved CTC production to a final titer of 25.9g/l. We anticipate that our work will provide a biotechnological potential of enzymatic evolution and strain engineering towards new TC derivatives in microorganisms.
Copyright © 2016,The Laboratory of Molecular Microbiology at Shanghai Jiao Tong University. All rights reserved.
Add:Science Building, Xuhui Campus, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 200030, China. Tel:021-62932943
